上节讲了状态管理,但是当 App 重启后,数据就都丢失了,这样就比较尴尬了,什么都要重来,所以这节我们来讲下数据持久化。数据持久化主要有如下方式
- 文件读写
shared_preferences存储- 数据库存储
持久化的实现都需要通过三方插件来实现,接着会慢慢介绍三种实现方式
文件读写/ IO 操作
文件读写需要 path_provider 插件,写这篇文章的时候,最新版本是 0.5.0+1,小伙伴们可以根据官网最新的版本进行替换,导入后我们就可以来看下如何实现文件的读写了。path_provider 的源码比较简单,这边就不单独拎出来说了,可以自行查看。path_provider 用于获取手机的存储文件位置,一共有三个方法
getTemporaryDirectory临时目录,在 Android 中对应的方法为getCacheDir,而在 iOS 中对应为NSCachesDirectory,可以通过系统检测并清除getApplicationDocumentsDirectory缓存目录,在 Android 中对应为AppData文件夹,在 iOS 中对应为NSDocumentsDirectory,只有当 App 被删除才能被删除getExternalStorageDirectory外部存储目录,只有在 Android 中有效,在 iOS 调用会抛出UnsupportedError异常,不过 Android 在写入前记得先申请权限哟,否则也是不行滴。
读写文件操作需要通过 Dart 的 IO 操作完成,这边小伙伴们可以自己看文档 File class,接着我们就直接通过例子来看文件实现数据持久化。先看下效果吧,最终重启 App 后,数据也能正常读取显示,说明数据被保存下来了
看下实现的代码,因为会涉及到多种方式,所以这边我把视图抽取出来实现
1 | Widget _fileIoPart() { |
关键的部分在于 _writeTextIntoFile 和 _readTextFromFile 两个方法的实现。看下实现的代码
1 | // 如果写入外部内存需要读写权限,这边使用了第三方插件 `permission_handler` |
因为外部存储的文件需要涉及到权限问题,而且 iOS 也不支持,所以如果需要使用文件来持久化数据的话,尽量使用另外两种。因为在例子中,我们保存的数据相对比较简单,所以这边就不得不说另外一种更方便的持久化方式了 shared_preferences
SharedPreferences
写 Android 的小伙伴对这个应该不陌生了,但是 Flutter 并没有自带的 shared_preferences 功能,需要第三方插件来实现,引入 shared_preferences 插件,写文章的时候最新版本是 ^0.5.1+2,还是先看下最后的效果
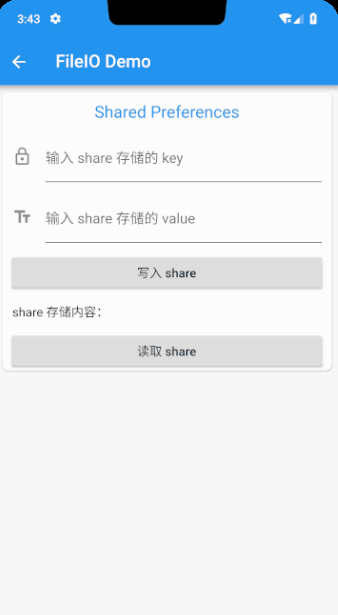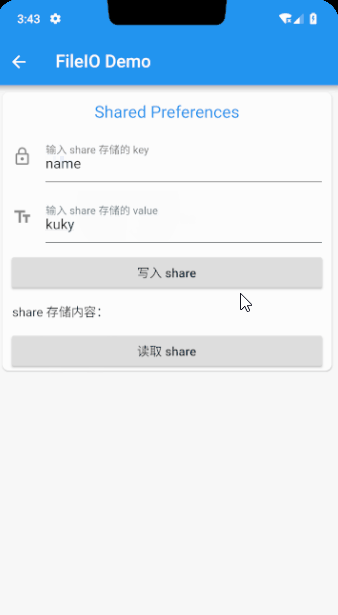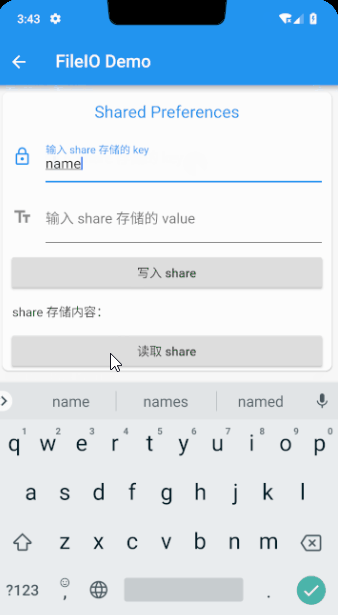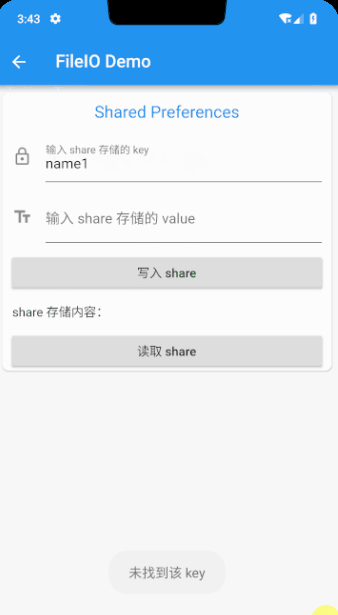
代码的实现相对比较简单
1 | Widget _sharedPart() { |
实现的关键部分就是方法 _writeIntoShare 和 _readFromShare
1 | void _writeIntoShare() async { |
这两种数据持久化的方式主要用于存储相对简单,关系不复杂的数据,如果涉及到大量的,且字段之间有关系的情况就需要通过数据库来实现了,Android 和 iOS 都自带 sqlite 数据库。
以上代码查看 data_persistence_main.dart 文件
Sqflite
Flutter 实现数据库存储需要通过插件 sqflite 来实现,写文章的时候最新的版本是 sqflite 1.1.3,但是该版本需要 flutter 1.2 以上才行,所以我选择的是 sqflite 1.1.0,小伙伴可以根据自己的 flutter 版本选择相应的 sqflite 版本
sqflite 的基本操作语句,在文档中已经写得非常明白了,所以就不搬运了,这边直接讲下对于数据库的一些封装处理吧,因为打开数据库是一个很消耗资源的一个过程,所以呢,推荐实现单例会比较好。例如我们要实现一个 student 存储表
1 | class DatabaseUtils { |
那么对数据库的操作就完全考验你的 SQL 的掌握程度了,但是千万记住,sqlite 中的类型只有,整型 integer ,字符类型 text,浮点类型 real,二进制 blob。数据库的具体例子会等到最后的实际项目中展示,原谅我不懂如何展示一个界面给你操作,实现数据库的各种功能。
该部分代码查看 db_util.dart 文件,里面有一些基本的操作写法,小伙伴可自行查看。

